Industrial Data Platforms and seaport community requirements and challenges
What is the role of Big Data in the port ecosystem and its evolution? As the Fourth Industrial Revolution is manifesting in ports, their digital transformation reveals opportunities for enhancement of the already existent business processes, as well, the life cycle operations of port logistics operations in scope of aggregating and processing data from different data sources.
Seaports, as the connecting tissue between all other modes of transport, contribute undeniably in the economy of the wider region that they are located in. In the recent decades, port activity in terms of international shipping trade has exploded, resulting in the rapid evolution of the port ecosystem and the ever-increasing complexity of their management. In this context, data-driven intelligence is introduced as a powerful tool in the process of managing and inspecting different aspects of the port operations’ lifecycle. This kind of intelligence introduces the need for data aggregation from different data sources that provide information about vessels, oceans, wave stations, observations from environmental conditions, fishing and maritime biodiversity, routes and trajectories, and incidental or voluntary oil spill events.
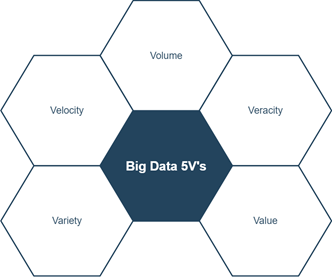
In terms of Big Data, the aggregated data can be described by the five V’s definition model that consists of the following data characteristics:
- Volume represents the magnitude of data that is generated and collected.
- Velocity denotes the pace at which the data flows.
- Variety indicates heterogeneity in data types, formats, structuredness, and data generation scale.
- Veracity refers to noise and quality issues in the data.
- Value denotes the value that can be obtained from processing and mining.
Diving deeper into some key application areas in scope of the value of the data that is harvested within the port ecosystem, the most important ones are considered to be the optimization of vessel selection for cargo shipment, ETA (Estimated Time of Arrival) calculation, freight forecast, selection of optimum vessel speed and fuel consumption, as well as, vessel maintenance. Concerning the yard side operations, significant optimization in the port’s activity is considered to be energy optimization in terms of resource management, such as the transport and stacking of containers, and energy supply planning.
The legislation and privacy norms concerning the storage and processing of the aforementioned data are becoming increasingly strict, and IT solutions that enforce privacy and consent policies are crucial. Solution towards the mitigation of the data infringement hazard is the blockchain technology that ensures the distributed and secure coordination between all the involved parties. The application of blockchain in the IoT sector are countless, while many technological aspects of the port’s ecosystem are revolutionized, such as the smart energy sector, the preservation of personal data, the operation of smart vehicles for tamper-proof data exchange, and the protection of the system from malicious transactions and attacks.
